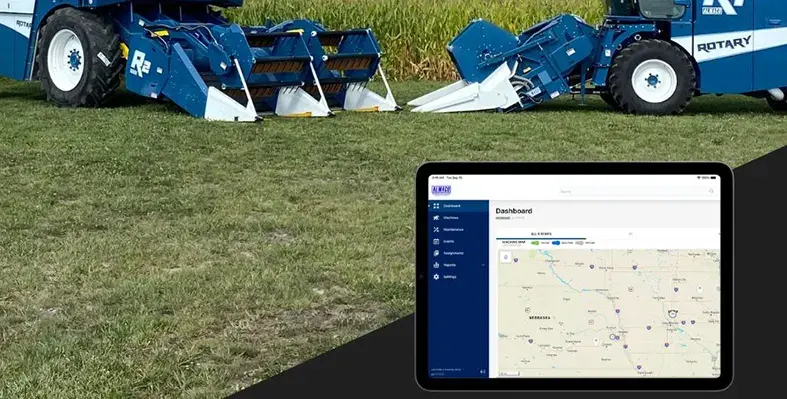
ALMACO Telematics boosts seed research efficiency
ALMACO Telematics is a next-generation system delivering remote access to real-time machine data—boosting efficiency, performance, and uptime for seed research professionals
Available on both the R1 Single-Plot and R2 Twin-Plot Research Combines, it’s the only telematics offering integrated specifically for seed research, reinforcing ALMACO’s leadership in precision agtech.
With insights into numerous machine parameters, the platform provides deep visibility into settings, location, diagnostics, software, and performance. This empowers fleet managers and researchers to easily monitor and optimise machine use for peak operational output.
Maximising uptime through smart diagnostics
A key feature of ALMACO Telematics is its remote diagnostics and repair capability, protecting uptime and reducing disruptions. Over 30% of service issues can be resolved remotely, removing the need for a field technician and delivering cost-effective value.
Simplified software upgrades
The system enables remote software updates, ensuring machines stay up to date without site visits. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs while supporting continuous tech improvement.
Enhanced fleet oversight
From their desks, managers can track machine performance and advise operators to refine seed trial accuracy. Telematics interfaces can also be remotely customised to support the specific goals of different research operations, improving data precision and machine functionality.
A smart investment for research operations
By reducing field calls, improving uptime, and enhancing resale value, ALMACO Telematics offers a strong return on investment. With its real-time oversight and proactive maintenance tools, seed research professionals can operate with confidence and lower costs.
“The integration of ALMACO Telematics marks a significant step forward in precision seed research,” said Mat Titus, service director at ALMACO. “By offering real-time data access and remote diagnostics, we are enabling researchers to focus on what matters most—developing the next generation of seed innovations.”